Medical Therapy
What are the goals for the treatment of IBD?
To date, scientists have not discovered a cure for IBD. Treatment of patients with IBD involves getting control of the inflammation or putting out the “fire” that leads to the symptoms and damage caused by this disease.
 Over time, poorly controlled inflammation has been shown to lead to the development of one or more complications which often require hospitalization and surgery. Research has shown that medications that work to control inflammation by suppressing a person’s immune response are among the most effective for successfully inducing (getting disease under control quickly) and maintaining (long-term control) disease remission. Medications have shown to be effective for inducing and maintaining disease remission in IBD. In the past, health care providers viewed avoidance of hospitalization and partial control of IBD symptoms as treatment success. Advances in the understanding of the disease and its treatments have lead to the development of different treatment goals for patients.
Over time, poorly controlled inflammation has been shown to lead to the development of one or more complications which often require hospitalization and surgery. Research has shown that medications that work to control inflammation by suppressing a person’s immune response are among the most effective for successfully inducing (getting disease under control quickly) and maintaining (long-term control) disease remission. Medications have shown to be effective for inducing and maintaining disease remission in IBD. In the past, health care providers viewed avoidance of hospitalization and partial control of IBD symptoms as treatment success. Advances in the understanding of the disease and its treatments have lead to the development of different treatment goals for patients.
These goals include the following:
- Rapid induction of disease remission (fast control of symptoms)
- Maintenance of disease remission (long-term control of symptoms)
- Steroid-free remission
- Healing of ulcers and all inflammation (mucosal healing)
- Avoidance of hospitalizations
- Avoidance of surgery
- Normalization of quality of life
Ideally these goals can be achieved while avoiding medication-related side effects. As time goes on, more effective and better-tolerated medications are being developed.
Drug treatment is the most common and effective method for treating IBD in the short and long-term. Your doctor may prescribe a number of different medications alone or in combination based on your needs. There are six main categories of drugs used in IBD:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce inflammation in the intestinal tract and throughout the body. Two main groups of anti-inflammatory drugs are used: glucocorticoids (steroids) and mesalamine-containing drugs. Glucocorticoids are often used to treat IBD flares; where as mesalamine-containing drugs are used to manage long-term inflammation.
- Immunosuppressant medications are used to reduce inflammation by decreasing the body’s immune response.
- Biologic drugs are used to decrease inflammation by blocking or activating specific molecules or receptors in the body. Biologic drugs work very specifically to decrease inflammation in the intestines.
- Antibiotics are useful in Crohn’s disease to help clear infections from a fistula or abscess.
- Pain relief medications are used to reduce the abdominal pain associated with IBD.
Treatment Approach
What is the Traditional Therapeutic Approach?
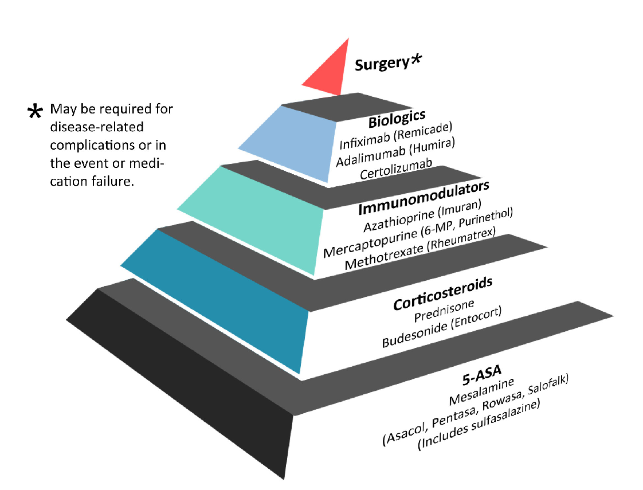
The “traditional therapeutic approach” to IBD consists of a step-wise or “pyramidal” approach. With this approach, all patients are treated with the weakest or least potent medications first. If symptoms do not improve then the next drug is tried. If drug number two does not work then drug number 3 is tried. This step-wise approach continues until the top of the pyramid is reached and no remaining medication options exist. Figure 1 illustrates this concept along with the specific medications used at each stage. These medications differ somewhat for CD and UC. The drawback to using this approace for everyone is that it does not take into account individual differences in disease severity and behavior (also known as disease phenotype). Some patients have more aggressive disease and therefore require a more tailored approach to treatment.
How is the Treatment of IBD changing?
The Step-Up Approach
Over the past decade more medications have become available for the treatment of IBD as a result of research and development. Some of these medications have been shown to be more effective for the management of different disease phenotypes and for the prevention of complications. Research has also suggested that certain groups of patients with IBD may benefit from being treated with selected medication sooner, before complications develop. The following groups of patients with IBD may benefit from earlier, more targeted intervention:
- Those who have required multiple surgeries
- Those with extensive disease (involvement of a larger portion of the GI tract)
- Those with disease involving an undesirable location (i.e., upper GI tract, small bowel, perianal disease)
- Those with specific disease-related complications (i.e., fistulizing disease)
What medications are used to treat IBD?
Antibiotics
How do antibiotics work?
Antibiotics are medications that work by killing “harmful” bacteria and depending on the type of antibiotic used can work differently. Antibiotics are reserved for the treatment of bacterial infections that your body needs help eliminating. There are several classes of antibiotics and the antibiotic chosen by your doctor depends upon what type and bacteria and infection your doctor is treating.
How are antibiotics taken?
Antibiotics can be taken by mouth in tablet form or intravenously. Antibiotics are given intravenously when there may be problems with oral absorption or when an infection is severe.
Are antibiotics effective for the treatment of UC?
Antibiotics are not effective for the treatment of UC itself. However, they are effective for the treatment of infectious complications of UC such as Clostridium difficile- induced diarrhea. C. difficile is a bacteria that forms spores which are resistant to elimination. We all carry C. difficile in our bowel. The organism only causes problems when it “overgrows”. C. difficile produces a chemical (toxin) that causes diarrhea. Patients with IBD are prone to developing C. difficile infection. Patients who have had their colons removed and now have an internal pouch made of small bowel (IPAA) may develop inflammation in the pouch, in part, to the overgrowth of bacteria in the pouch. Antibiotics have been shown to be very effective for the treatment of this condition call “pouchitis”.
Are antibiotics effective for the treatment of CD?
Antibiotics are generally not effective for the treatment of CD itself. However, they are effective for the treatment of infectious complication of CD, such as abscesses and perforation (Module 1). Patients with CD are also predisposed to developing C. difficile infections as well.
How expensive are antibiotics?
The cost of antibiotics can vary depending on the type of antibiotic prescribed.
What are the potential side effects of antibiotics?
Antibiotics are generally well tolerated but some individuals may have allergies to penicillins and other components of antibiotics. Unpleasant symptoms such as nausea, headache, and diarrhea are possible. Antibiotic therapy can cause an alteration in the balance between “good” bacteria and “bad” bacteria. This can lead to the overgrowth of some bacteria and fungi (yeast) which can lead to the development of infection. Bacteria are smart and have good survival skills. They are able to adapt and may become resistant to antibiotic therapy. Sometimes your doctor will prescribe different antibiotics in a rotating fashion in order to prevent bacteria from having the time to “outsmart” the antibiotics. This approach is especially important if long-term antibiotic therapy is required.
5-aminosalicylic acid derivatives (5-ASA)
How does 5-ASA work?
Mesalamine is the active component of sulfasalazine. This drug is thought to work by decreasing inflammation and irritation of the intestine through its direct affect on the intestinal lining (mucosal surface). These drugs are designed to be released in the last part of the small bowel and colon. It works by reducing inflammation. Approximately 20 percent of the drug gets absorbed from the intestinal tract into the rest of the body. This drug is broken down and removed from the body by the liver and special cells in the intestine and leaves the body through the urine.
How is 5-ASA taken?
5-ASA can be taken by mouth in pill form or rectally in either enema or suppository form. The route depends on the location of the disease. Patients with inflammation confined to the rectum and sigmoid can take a topical formulation alone in order to achieve disease remission. However, those with more extensive disease are more likely to achieve disease remission if oral and topical formulations are taken at the same time.
Some 5-ASA formulations are taken two to three times per day given the short duration of effect of these medications. However, newer formulations have been developed that only need to be taken once a day. Taking fewer pills less frequently may be easier to remember and better tolerated by patients.
Are 5-ASAs effective for the treatment of UC?
5-ASAs have been and continue to be the best treatment for patients with mild to moderately severe UC. They have been proven in many well-designed studies to be effective for inducing and maintaining disease remission when compared to placebo (a fake pill).
Are 5-ASAs effective for the treatment of CD?
5-ASAs, although still widely used for the treatment of CD, are generally ineffective for treatment of CD. It is possible that patients with very mild disease may benefit from this class of drug, although to date, research has not proven this.
How expensive are 5-ASAs?
Depending on the type, dose, and route of administration they may cost anywhere from 30 to 220 Canadian dollars per month.
What are the potential side effects of 5-ASAs?
5-ASA medications are generally well tolerated with very few serious side effects. Some uncommon serous side effects include allergic reaction in the kidneys (interstitial nephritis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), inflammation of the sac that surrounds the heart (pericarditis) and inflammation of the lungs (pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease, bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia or BOOP). More commonly 5 out of 100 people will develop worsening diarrhea. Nuisance symptoms of drug intolerance include nausea, rash, fever, and headache. The following table portrays the most important side effects of 5-ASA therapy.
Table 1
| Medication | Common Side Effects | Rare Side Effects | Important Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-ASA |
|
|
|
What is sulfasalazine(SSZ) and how does it work?
SSZ is a 5-ASA with an added sulfa component (a type of antibiotic). This drug was first used to treat patients with arthritis given its benefit for relief of joint pain.
How is it taken?
SSZ is taken in pill form. Is SSZ effective for the treatment of UC? SSZ is effective for the treatment of UC. However, the ability to take an adequate dose may be limited by dose-related side effects. SSZ could be considered when patients with mild to moderate UC symptoms are experiencing joint pain as well.
Is SSZ effective for the treatment of CD?
SSZ may be effective for the treating mild to moderate CD of the colon as suggested by one small study. The use of SSZ can be considered in patients with mild colonic CD symptoms who also are having difficulty with joint pain.
How expensive is SSZ?
SSZ costs between 75 and 145 CAN dollars per month.
What are the side effects of SSZ?
Patients generally experience more side effects with SSZ use as a result of the sulfa component. Side effects are often dose-related (the higher the dose of the drug the greater the chance of experiencing a side effect). The most common side effects are headache, nausea and drug rash. A less common but serious side effect is anemia (when the bone marrow stops making blood cells). Some of these side effects can be minimized by increasing the dose of SSZ slowly.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids (steroids), like prednisone® or budesonide®, are strong inhibitors of inflammation. They work by suppressing the immune system. These medications are widely used for the treatment of many inflammatory diseases and have been in use for many years in order to induce remission in patients with IBD. They are effective for controlling IBD related symptoms in the short term but are not effective for long-term use. They are associated with many short-term and long-term side effects. In addition to this, they very effective for the healing of intestinal ulcerations which research has shown to be an important goal when treating patients with IBD.
How do corticosteroids work?
Steroids decrease inflammation by preventing infection fighting white blood cells from getting into tissues where they would normally cause more inflammation and damage. As a result these drugs decrease swelling, redness, pain and many of the symptoms of IBD.
How are corticosteroids taken?
There are different formulations of steroids. They can be taken either orally, intravenously or rectally. Prednisone® is one of the most widely used formulations of oral steroid and is in pill form. Prednisone is well absorbed from the intestine. Budesonide® is another form of steroid that is taken in pill form. Unlike prednisone, budesonide is designed to be released in the last part of the small bowel (ileum) and right colon where it attaches to the bowel wall and exerts it affect. The liver immediately breaks down more than 90 percent of this medication. Therefore there are fewer side effects associated with the use of this medication. Other formulations of oral and intravenous steroids are available as well.
Are corticosteroids effective for the treatment of UC and CD?
Steroids are highly effective for the induction of clinical remission in patients with UC and CD. However, they are not effective for long-term use. The requirement for steroid treatment may mean that a patient has more aggressive disease.
How expensive are corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids are inexpensive and may cost 10 to 20 Canadian dollars per month.
What are the potential side effects of corticosteroids?
Side effects of steroids occur quite frequently and can be divided into short-term and long-term side effects. In the short-term, patients can gain weight, develop acne, and experience mood swings and insomnia. Long-term side effects include development of high blood pressure, cataracts, diabetes, heart failure, obesity, thinning of the bones (osteoporosis) and dependence on steroids for normal bodily functions.
One or More Important Side Effects Corticosteroids

This pictograph shows the number of people (in blue) who will develop at least one side effect of corticosteriod treatment (out of 1000 people).
One or more side effects
Immunosuppressants
What are Immunosuppressants?
This class of medication controls disease activity by modifying and suppressing the immune system, as do most of the effective medications used to treat IBD. This class of medication includes methotrexate (MTX), azathioprine (AZA), and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP).
Methotrexate (MTX)
What is MTX and How does MTX work?
MTX is an immunosuppressant that decreases the body’s ability to manufacture genetic material (DNA) necessary for white blood cells to multiply. It does this by decreasing the body’s use of folate. In CD it is felt to both change the immune response and to decrease inflammation. MTX is broken down by the liver and bacteria in the bowel and leaves the body through the urine.
How is MTX taken?
For the treatment of CD, MTX is taken in injection form. The drug is injected just under the skin (subcutaneously) using a small needle. MTX is taken once per week. For induction of disease remission MTX is given at a dose of 25 milligrams once per week. For maintenance of remission the dose may be decreased to 15 milligrams once per week.
Is MTX effective for the treatment of UC?
MTX has not been well studied for the treatment of UC.
Is MTX effective for the treatment of CD?
MTX has been well studied for the induction and maintenance of remission in CD and has been shown to be effective for both when compared to placebo (fake medicine).
How expensive is MTX?
MTX costs approximately 80 CAN dollars per month for the injectable formulation and between 200 and 300 dollars per month for the oral formulation.
What are the potential side effects of MTX?
The most common side effects of MTX include nausea and fatigue. These symptoms tend to be most severe the first dew days following an injection. Taking folic acid and anti-nausea medication may sometimes help to improve these symptoms. More severe reactions include inflammation of the liver, thyroid gland and lungs and decreases in blood counts. However, these side effects do not occur very frequently. Please refer to the following pictograms to see your risk of developing these more serious side effects while taking MTX.
Important Side Effects - Methotrexate

This pictograph shows the number of people out of 1000 who will develop a side effect while taking methotrexate. People in green are those that will develop liver fibrosis. People in blue are those that will develop lung fibrosis. People in purple are those that will develop thyroid problems.
Liver fibrosis
Lung fibrosis
Thyroid function abnormalities
Azathioprine (Imuran)
What is azathioprine and how does azathioprine work?
Azathioprine (also known as Imuran) is another member of the Immunomodulator class. It works by preventing the use of purines, the building blocks of DNA and proteins. It may also prevent cells like white blood cells from multiplying. Both the benefit and the side effects of the drug are delivered through the creation of something called 6-TGN which is created through the metabolism of azathioprine.
How is azathioprine taken?
Azathioprine is taken in pill form. Most patients can take this once per day. Previous studies suggest that doses in the range of 2 to 2.5 milligrams per kilogram of body weight are most effective. However, there is a special enzyme that was discovered to break down azathioprine. This enzyme is called TPMT. Rarely, patients may lack this enzyme. Patients who do not have enough of this enzyme will need their dose adjusted. Patients who lack this enzyme completely should not take the drug at all. Many doctors check the level of this enzyme before starting the drug or at least before giving a full dose of the drug. Blood work to monitor the white blood cell count and liver enzymes are necessary when taking this drug. Azathioprine, at the correct dosage, can take anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks to become effective.
Is azathioprine effective for the treatment of UC?
Azathioprine has been shown to be modestly effective for the maintenance of remission in UC.
Is azathioprine effective for the treatment of CD?
Azathioprine has been shown to be effective for the treatment of CD.
How expensive is azathioprine?
Azathioprine is not overly expensive with costs ranging from 24 to 80 CAN dollars per month. 6-MP is more expensive costing between 138 and 260 CAN dollars per month.
What are the potential side effects of azathioprine?
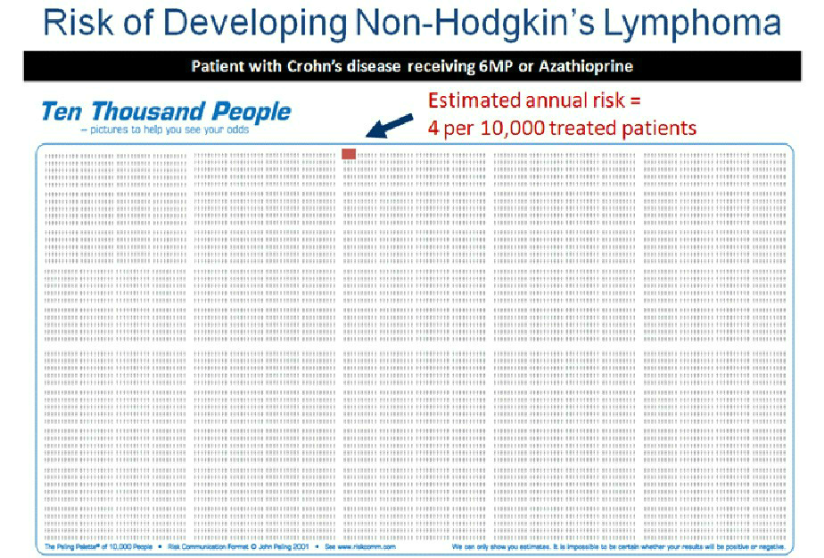
Some of the side effects of Azathioprine include nausea, joint pain, rash, and fever. Serious, but rare, side effects can include decreased white blood cell count, inflammation in the liver (hepatitis), lymphoma (cancer of the white blood cells) and infection. Please refer to the following pictograms to see your risk of developing these more serious side effects while taking azathioprine.
Mercaptopurine (6-MP, Purinethol)
Mercaptopurine (MP) is similar to azathioprine, and works the same way as azathioprine. The risks and benefits are the same as well. The only differences are related to dose and the potential for nuisance side effects. MP is given at a dose of 1 to 1.5 milligrams per kilogram. Since there is no extra step required to break down this drug there may be fewer symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Important Side Effects Associated with Azathioprine and 6-MP

Pancreatitis
Serious infection

Allergic reactions
Nausea
Hepatitis
Siegel CA, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:874-81
Biologics
Infliximab (Remicade or Inflectra)
What is Infliximab (IFX) and how does it work?
Infliximab is a protein consisting human and mouse fragments (chimeric antibody) designed by scientists to target a specific type of inflammatory substance called tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). TNF-α is responsible for creating inflammation in a number of ways. TNF-α has been shown to be present in large amounts in the bowel and blood stream of patients with IBD. Infliximab works by destroying TNF and decreasing inflammation.
How is infliximab taken?
Infliximab is given through the vein as an Intravenous (IV) infusion. The dose of Infliximab is weight based at 5 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. Three doses are given close together at the beginning (loading doses) at time zero, two weeks and then six weeks.
| 0 | 2 | 6 | 14 | 22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
The effect of the drug is then assessed and a decision about ongoing maintenance therapy is made. Patients receive an infusion once every eight weeks as maintenance therapy.
Is infliximab effective for the treatment of UC?
Infliximab has been shown to be effective for the induction and maintenance of steroid-free clinical remission in patients with moderate to severe UC. It has also been associated with decreased need for hospitalization and surgery as well as improved quality of life.
Is infliximab effective for the treatment of CD?
Infliximab has been shown to be effective for the induction and maintenance of steroid-free clinical remission in CD. It is also one of the only drugs shown to be effective for the treatment of fistulizing complications.
How expensive is infliximab?
Each 100-milligram vial of the drug costs approximately 900 CAN dollars. A year of therapy can cost up to 35,000 CAN dollars.
What are the potential side effects of Infliximab?
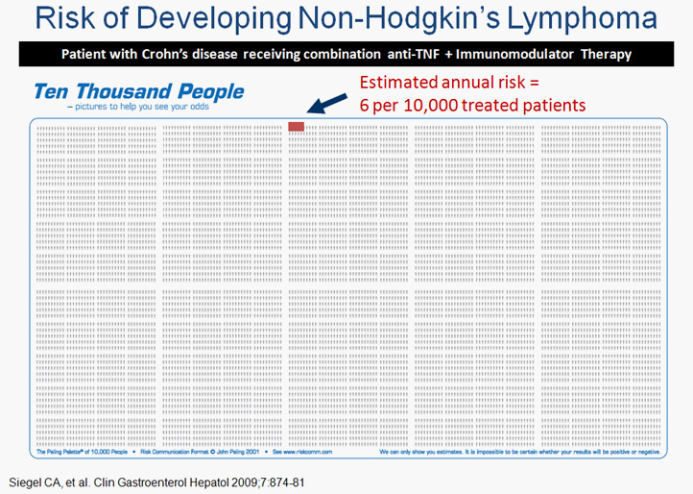
Important but uncommon side effects associated with the use of infliximab include infusion reactions, infections, neurological symptoms, drug-induced lupus and a possible increase in the risk of lymphoma. Please see the following pictograms to see your risk of developing these side effects while taking infliximab.
Important Side Effects Associated with Anti-TNFAgents

Drug-induced lupus-like reaction
Infusion reactions
Serious infection
Adalimumab (Humira)
What is adalimumab (ADA) and how does it work?
Adalimumab is the second anti-TNF drug to become available for the treatment of CD in Canada. ADA is also an anti-TNF agent but the protein is comprised of mostly human protein. ADA works the same way that IFX works.
How is adalimumab taken?
ADA is administered as an injection given just beneath the skin (subcutaneous). It is given initially as two loading doses of 160 mg at time zero and 80 mg at two weeks. If maintenance therapy is continued the standard dose is 40 mg every second week.
Is adalimumab effective for the treatment of UC?
Adalimumab (Humira) was shown to reduce symptoms and induce (lead to) and maintain (continue) remission in patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis.
Is adalimumab effective for the treatment of CD?
ADA is effective for the induction and maintenance of clinical remission in CD. It has been demonstrated to be effective as primary therapy (first anti-TNF agent used) and secondary therapy (second line anti-TNF agent).
How expensive is adalimumab?
Adalimumab costs approximately 850 CAN dollars (every two weeks). ADA may cost up to 18, 300 CAN dollars for a year of therapy.
What are the potential side effects of adalimumab?
So far the side effect profile for adalimumab is very similar to that of Infliximab with one exception. Given that this drug is injected beneath the skin, rather than directly into a vein, there is no risk of developing an immediate infusion reaction.
Golimumab (Simponi)
What is golimumab (Simponi) and how does it work?
Golimumab is another anti-TNF that works similarly to infliximab and adalimumab.
How is golimumab (Simponi) given?
Golimumab is given as a subcutaneous (S/C) injection. A patient receives two injections the first week of treatment followed by one injection the following week (induction). Maintenance dosing is one injection every 4 weeks.
Is golimumab effective for treatment of Ulcerative Colitis (UC)?
Golimumab has been shown to be an effective treatment for reducing symptoms and inducing remission in patients with ulcerative colitis.
Is golimumab effective for treatment of Crohn’s disease (CD)?
Golimumab is only indicated for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
How much does golimumab cost?
One 100-milligram injection (given every 4 weeks) costs approximately 1900 CAN dollars.
What are the potential side effects of golimumab?
Side effects of golimumab are similar to those of infliximab and adalimumab including injection site reactions.
Certolizumab (Cimzia)
Certolizumab is another, third generation, anti-TNF agent effective for the treatment of CD. It differs from the other anti-TNF drugs primarily by its structure. It works is the same as the other anti-TNF drugs. It is given once a month.
Vedolizumab (Entyvio)
What is vedolizumab (Entyvio) and how does it work?
Vedolizumab is a biologic medication that targets inflammation (swelling) directly in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Vedolizumab blocks a protein on the surface of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that cause the inflammation. This prevents those lymphocytes from travelling into the inflamed areas of the GI tract, and so the amount of inflammation is reduced.
How is vedolizumab given?
Vedolizumab is given as an intravenous infusion. Initially, infusions are given at weeks 0, 2, and 6 (induction) and then once every 8 weeks (maintenance). The infusions will take place at a private infusion clinic. There are infusion clinics throughout Nova Scotia.
Is vedolizumab effective for treatment of Ulcerative Colitis (UC)?
In adults with moderate to severe UC, vedolizumab has been shown to be effective in relieving symptoms caused by flare-ups, achieving early and lasting remission, improving the appearance of intestinal lining damaged by your disease, and reducing or eliminating the need for steroids.
Is vedolizumab effective for the treatment of Crohn’s Disease (CD)?
In adults with moderate to severe CD, vedolizumab has been shown to be effective in relieving symptoms caused by flare-ups, achieving early and lasting remission, and reducing or eliminating the need for steroids.
How expensive is vedolizumab (Entyvio)?
One 300mg vial of Entyvio (given every 8 weeks) costs approximately 3300 CAN dollars.
What are the potential side effects of vedolizumab?
Possible side effects of vedolizumab include: common cold, headache, joint pain, nausea, fever, infections of the nose and throat, tiredness, cough, bronchitis, fever, flu, back pain, rash, itching, sinus infection, throat pain, and pain in extremities.
Important but uncommon side effects of vedolizumab include infusion and serious allergic reactions. There is a chance that vedolizumab could cause inflammation of the liver.
Although vedolizumab works specifically in the gut, and it does not appear that the drug suppresses the immune response outside of the gut, there is still the chance that vedolizumab may cause an increased risk of infection. To date, data about the safety of vedolizumab has been quite promising. The rates of serious infections in patients on vedolizumab appear to be similar to those patients who received placebo (control) drug in clinical trials.
Drugs similar to vedolizumab were thought to increase a person’s chances of getting a rare and serious brain infection called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). However, this has not been seen in any of the many patients treated that have been with vedolizumab, so it is unlikely that this is a real risk, however it cannot be ruled out.
| Adverse Event | Number out of 100 | Absolute Risk Difference | Risk on Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infusion Reactions | 4/100 | 1/100 | 3/100 |
| Inection (serious) | 7/100 | 5/100 | 1.5/100 |
| Liver Damage | 0.5/100 | 0.5/100 | 0/100 |
| Liver Enzyme Changes | 0.2/100 | 0.2/100 | 0/100 |
| Liver Failure | 0.03/100 | 0.03/100 | 0/100 |
| Cancer | &< 1/100 | No increased risk observed | 1/100 |
Ustekinumab (Stelara)
What is ustekinumab (Stelara) and how does it work?
Ustekinumab is a different type of biologic medication that targets a chemical messenger called IL-12/23. It is thought that IL 12/23 is one of the causes of inflammation in IBD.
How is ustekinumab taken?
A patient beginning treatment starts with a one-time intravenous (IV) infusion dose (induction) based on the patient’s weight, followed by subcutaneous (under the skin) injections (maintenance) every 8 weeks. The first IV dose is administered at an infusion clinic. Following that, the injections every 8 weeks can be given by a health care professional or self-injected by the patient after proper training.
Is ustekinumab effective for the treatment for Ulcerative Colitis?
Currently, ustekinumab has only been approved for use in Crohn’s diease.
Is ustekinumab effective for the treatment for Crohn’s Disease?
Ustekinumab is indicated for patients with moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease who did not respond to or could not tolerate other medications used to treat Crohn’s disease.
In clinical trials, ustekinumab was shown to improve Crohn’s disease symptoms and induce remission.
How expensive is ustekinumab?
One 90-milligram injection (given every 8 weeks) costs approximately 5000 CAN dollars.
What are the potential side effects of ustekinumab?
Side effects of ustekinumab include: upper respiratory infections, headache, dizziness, tiredness, joint or back pain, nausea, itching, and redness at the injection site.
Ustekinumab can make you more likely to get infections or make an infection that you have worse.
Ustekinumab is a selective immonomodulator meaning that it changes a specific part of the immune response in your immune system. There is always the risk that these types of drugs could increase a person’s chance of getting certain cancers such as non-melanoma skin cancers. However, in clinical trials, the rates of cancer in people treated with ustekinmab were no different than those of the general population.
Biosimilars
What are biosimilars?
As drug patents (license for a period of time which excludes other companies from making a similar drug) expire, manufacturers are developing biosimilar products which are similar to the original (innovator or reference) biologic medication. Biosimilars are also sometimes referred to subsequent entry biologics (SEBs). Currently the only biosimilar approved in Canada is Inflectra (infliximab) which is the biosimilar of Remicade. The patent for adalimumab (Humira) is set to expire in Canada in 2017. Health Canada approves biosimilars after a thorough comparison to a reference drug.
Are biosimilars different from generic drugs?
Biologic drugs are made up of large, complex structures (molecules) that come from living cells. It is a very complicated process to manufacture a biologic which is why they are very expensive medications. It is very difficult to make an exact copy of a biologic medication.
Small molecule drugs such as Tylenol are made up of simple chemical structures. Generic medications contain the same active ingredient as the original small molecule drug which in the example of Tylenol is acetaminophen.
In Canada, biosimilar drugs are not considered “generic biologics.” They may be similar to the innovator biologic but they are not exact duplications. Manufacturers of biosimilars must demonstrate to Health Canada that their drug is similar to the original biologic.
Insurance Coverage/Financial Assistance
Once the decision has been made that a patient requires a biologic medication, the patient will be enrolled in a patient support program and connected with a nurse coordinator. This coordinator will advise patients about securing insurance or applying for financial assistance. The patient support program will assist patients with completing the necessary paperwork and insurance forms. Patients who do not have a private insurance plan will be asked to apply to the Nova Scotia Pharmacare Program.
Other Biologics
There are currently other types of biologics under study in clinical trials in Canada.
Here are a few examples of some of these drugs:
- Etrolizumab
- An oral anti-TNF
Talk to your IBD team to see if a clinical trial might be right for you!
Special Issues
Special Issues
Immunogenicity
Anti-TNF drugs are made of proteins that are foreign to our bodies. As a result, our own bodies may try to destroy or eliminate these drugs by forming their own proteins called antibodies. Antibodies target anti-TNF drugs and eliminate them. The chances of developing antibodies to these drugs (a process call immunogenicity) increases if patients receives drug doses that are spaced too far apart, do not receive “loading doses” (more drug at the beginning of therapy), or do not receive therapy with an immunosuppressant at the same time. The most important of these factors relates to how far apart doses are spaced and how regularly the drug is given (schedule of therapy).
Monotherapy versus Combination Therapy
Giving infliximab in combination with azathioprine to people who have never taken either drug before appears to result in a better response to infliximab when compared to giving infliximab alone. This has never been studied with humira. There may also be some small benefit to giving azathioprine or methotrexate in combination with an anti-TNF drug in order to prevent immunogenicity. However, taking more than one kind of immunosuppressant has been shown to increase the risk of developing serious infections, especially in people with severe IBD and in older patients. Therefore, the risk versus the benefit of each approach must be weighed and discussed with your doctor. If a person has severe IBD, then clearly the benefit of taking more than one drug outweighs the risk. At this time it is unclear how long one should stay on combination therapy once started.
Hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma (HSTCL)
HSTCL is an extremely and severe rare form of lymphoma (cancer of the white blood cells). The total number of reported cases has increased over the past decade. To date a total of 26 cases have been reported. The majority of these cases have included patients who have a diagnosis of IBD and have been treated with immunosuppressive medications (AZA, MTX or anti-TNF). In all cases of HTSCL, the patients have died. There appears to be a larger number of young males amongst these cases although HSTCL has been reported in older patients and in females as well. There simply have not been enough cases to determine what the cause of HSTCL is.
What are the risks and benefits of each of these medications?
Each medication carries the potential for side effects. However, the risk of the development of side effects must be balanced with the potential benefit the drug may have and the risk associated with not treating the disease. Table 2 lists all IBD medications and the most important side effects associated with their use.
Table 2.
| Medication Group | Common Side Effects | Rare Side Effects | Important Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 ASA (Salofalk, Asacol, Pentasa) |
|
|
|
| Sulfasalazine (SSZ) |
|
|
|
| Corticosteroids (Prednisone/Entocort) |
Short Term
|
|
|
| Immunomodulators Imuran, 6-MP |
One or more “Nuisance side effects” 20-30% (20 – 30/100)
|
|
|
| Methotrexate |
One or more “Nuisance side effects” 20-30% (20 – 30/100)
|
|
|
| Biologics |
|
|
|
| (Humira, Remicade) |
(3-21/100)
|
|
|
* Unclear if disease-related or drug-related
How long do I have to take these medications and what are the long-term risks?
IBD is a chronic disease that is present throughout a person’s lifetime. The disease most commonly flares and remits (gets worse and then gets better for a period of time). Ongoing medication therapy or maintenance therapy is advisable in order to prevent disease flares or to minimize the number of flares that a person will develop over their lifetime. Better control of inflammation also results in fewer complications, hospitalizations, surgeries and most importantly quality of life. Only a few studies have been completed that address the question of how long a person will stay in remission once an effective maintenance medication has been discontinued, but more research is ongoing. To date, Imuran has been studied and the research suggests that patients are much more likely to flare again within a year once medication has been discontinued compared to those who continue the medication.
References
References
- Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Rawsthorne P, Wajda A. Epidemiology of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in a central Canadian province: a population-based study. Am J Epidemiol 1999;149:916-24.
- Bernstein CN, Nabalamba A. Hospitalization, Surgery, and Readmission Rates of IBD in Canada: A Population-Based Study. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:110-8.
- Candy S, Wright J, Gerber M, Adams G, Gerig M, Goodman R. A controlled double blind study of azathioprine in the management of Crohn’s disease. Gut 1995;37:674-8.
- Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, et al. Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology2007;132:52-65.
- Cosnes J, Nion-Larmurier I, Beaugerie L, Afchain P, Tiret E, Gendre JP. Impact of the increasing use of immunosuppressants in Crohn’s disease on the need for intestinal surgery. Gut 2005;54:237-41.
- D’Haens G, Baert F, van Assche G, et al. Early combined immunosuppression or conventionalmanagement in patients with newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease: an open randomised trial. Lancet 2008;371:660-7.
- Faubion WA, Jr., Loftus EV, Jr., Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Sandborn WJ. The natural history of corticosteroid therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology 2001;121:255-60.
- Feagan BG, Fedorak RN, Irvine EJ, et al. A comparison of methotrexate with placebo for the maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease. North American Crohn’s Study GroupInvestigators . N Engl J Med 2000;342:1627-32.
- Feagan BG, Rochon J, Fedorak RN, et al. Methotrexate for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. The North American Crohn’s Study Group Investigators. N Engl J Med1995;332:292-7.
- Feagan BG, Yan S, Bala M, Bao W, Lichtenstein GR. The effects of infliximab maintenance therapy on health-related quality of life. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:2232-8.
- Hanauer SB, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn’s disease: the ACCENTI randomised trial. Lancet 2002;359:1541-9.
- Jones JL, Loftus EV, Jr. Lymphoma risk in inflammatory bowel disease: is it the disease or itstreatment? Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007;13:1299-307.
- Lashner BA, Shaheen NJ, Hanauer SB, Kirschner BS. Passive smoking is associated with an increased riskof developing inflammatory bowel disease in children. Am J Gastroenterol 1993;88:356-9.
- Lichtenstein GR, Feagan BG, Cohen RD, et al. Serious infections and mortality in association with therapies for Crohn’s disease: TREAT registry. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4:621-30.
- Munkholm P, Langholz E, Davidsen M, Binder V. Frequency of glucocorticoid resistance and dependency in Crohn’s disease. Gut 1994;35:360-2.
- Rutgeerts P, Diamond RH, Bala M, et al. Scheduled maintenance treatment with infliximab is superior to episodic treatment for the healing of mucosal ulceration associated with Crohn’s disease. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;63:433-42; quiz 64.
- Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2462-76
- Sandborn WJea. SONIC: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial Comparing Infliximab andInfliximab and Azathioprine to Azathioprine in Pastients with Crohn’s Disease Naïve to Immunomodulators and Biologic Therapy. 2008:A29.
- Sutherland LR, Ramcharan S, Bryant H, Fick G. Effect of cigarette smoking on recurrence ofCrohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 1990;98:1123-8.
- Remicade (infliximab) for IV injection [prescribing information]. Malvern, pA: Centocor 2005.
- Humira (adalimumab) [prescribing information]. North Chicago, IL: Abbott Laboratories 2005.
Last updated: September 22nd, 2017